Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) and is one of the leading causes for liver cancer and the most common reason for liver transplant. Currently, there are no vaccines on the market for HCV. The virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis infection, ranging in severity from mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. The Hepatitis C virus destroys liver cells and leads to inflammation in the liver. Most people are unaware they have been exposed to HCV virus. It is estimated that approximately 25% of people exposed to HCV will clears up the virus without medical intervention within a few months. If virus does not clear up within 6 months, hepatitis C progresses into the chronic state. There are different genotypes of HCV ranging from 1 to 6 and approximately 70% to 75% of all HCV patients carry genotype 1 virus(1).
Prior to 2011, treatments with ribavirin and interferon offered a low cure rate but had severe side effects. Newer treatments came to the market in 2011 but those required new medications to be taken in addition to the old ones. The cure rate increased slightly but side effects increased also. Many patients, especially ones with advanced liver disease, could not tolerate these treatments due to the severity of side effects. The cost of these treatments varies greatly from an estimated $15,000 to $60,000.
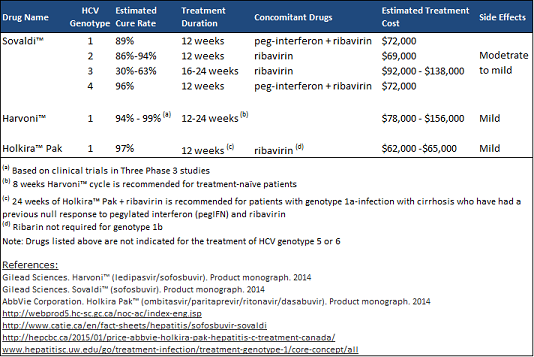
Since December 2013, Health Canada approved 3 additional drugs which offer an increased cure rate and are tolerated significantly better due to the reduction in treatment duration and, in some cases, elimination of drugs causing severe side effects:
On December 22, 2014, Reuters announced that Express Scripts, the largest pharmacy manager in US, will no longer cover treatments of SovaldiTM and HarvoniTM for HCV genotype 1 patients. The US division of Express Scripts had secured a discounted price of ViekiraTM Pak, the US equivalent of the Canadian HolkiraTM Pak(2). At this time, it is unknown if similar actions will be taken in Canada by Express Scripts Canada.
Another interesting development was made in Canada on February 12, 2015 when the Government of Prince Edward Island announced that they will invest $1.6 million dollars per year for the next three years in a new Hepatitis C disease management program(3). In his public statement, Minister Currie stated that “To help this ambitious project succeed, we needed a strong partner and we found that partner in AbbVie.” AbbVie is the manufacturer of HolkiraTM Pak (Canada) and ViekiraTM Pak (US). No details pertaining to a preferred pricing arrangement were announced.
We will continue to monitor the development of various treatment options for HCV and report our findings.
(1) http://www.hepatitisc.uw.edu/go/treatment-infection/treatment-genotype-1/core-concept/all
(2) http://www.reuters.com/article/2014/12/22/us-express-scripts-abbvie-hepatitisc-idUSKBN0K007620141222
(3) http://www.gov.pe.ca/health/index.php3?number=news&dept=&newsnumber=10059&lang=E